Learning Intention: We are learning to search the text to answer questions, and identify the 3-4 most important points/facts in a text.
Success Criteria:
# I can search the text for answers to questions, using the keywords in the question to help me.
# I can identify the 3-4 most important pieces of information in a text and write them in dot points.
(Monday) Independent Reading – 20mins
Prompt question (after reading) = Summarise the important events in the story (in the part you just read)
Reading Activity – Watch the video and answer the questions
(–> if you’re having internet troubles click here for a transcript of the video)
MONDAY – Endangered Seeds (BTN)
Q1 – How many plant species in WA are considered threatened with extinction?
Q2 – What are some challenges or difficulties with collecting seeds?
Q3 – Why is this project considered to be so important?
Q4 – Summarise the most important 4 details.
Our sound of the week is long “oo” sound as in moon. The sound /oo/ can be represented by more than one spelling. /oo/ could be , <oo> <oe> <ow <o-e><ui> <ou> Choose 8 words from the list below to practice this week:
- kangaroo
- moon
- screw
- pollute
- horseshoe
- balloon
- juice
- chewing
- salute
- brooding
- withdrew
- lawsuit
- coupe
- gruesome
- manoeuvering (British spelling)
- foolproof
- magnitude
- unscrewing
Today’s task is to find the syllables and segments (sounds) in your words. Let’s practise this using our new structure. See below a video for this task.
Writing: We are learning about simple and compound sentences.
I can:
-
- Identify simple sentences
- Identify compound sentences
Simple sentences:
Simple sentences have only one clause. This means that they have one
subject and a verb.
Example: The lion growled.
Compound Sentences:
Compound sentences are two or more simple sentences joined with a
conjunction.
Example: The lion growled but the mouse wasn’t scared.
Click here to download your worksheet. Read the sentences in the table below and tick the boxes to show whether they are compound or simple sentences.
This activity can be completed on seesaw as a PDF or printed in your homework book. Take a photo of your work to send to your teacher.
Extension: If you find this activity quick and easy, practice writing 3 compound sentences about your Passion project topic.
 Practice your counting goal for 5 min.
Practice your counting goal for 5 min.
Learning Intention:
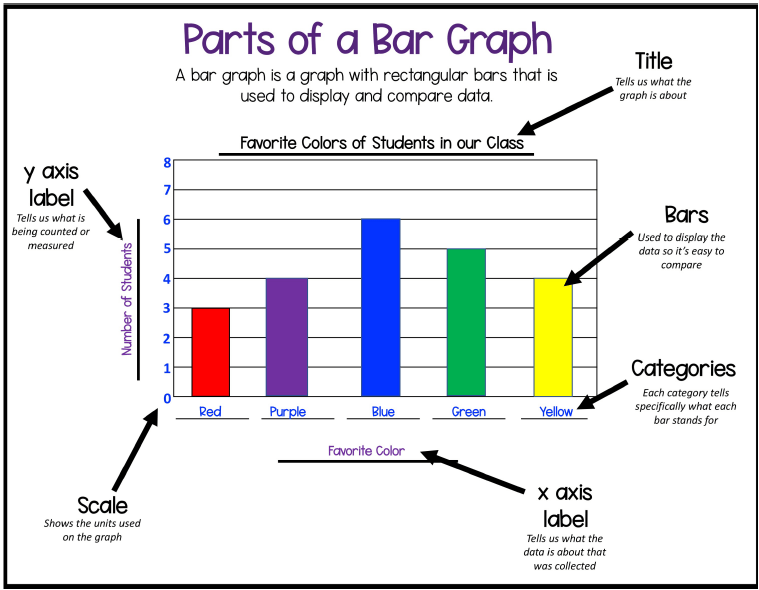
We are learning to interpret data and represent it in a bar graph.
Success Criteria:
I can:
- Represent the data in a Bar graph.
- Draw a vertical axis (y axis) and horizontal axis (x axis) correctly.
- Draw numbers along the y axis and the choices along the x axis.
- Draw straight lines using a ruler.
- Include a title for my graph.
- Clearly label the x axis and y axis.
- Present my work neatly.
Data Display and Bar Graph
Bar graphs can be used to show how something changes over time or to compare items. They have an x-axis (horizontal) and a y-axis (vertical).
Watch this video below to refresh your memory on how to create a bar graph:
Example of a Bar graph:
Activity: A group of students were surveyed to find out the most favourite flavour of ice-cream in their year level.
Here is the data collected:
1. Use this data to create a bar graph in your homework book or on graph paper (link provided below).
Click here to print Graph paper
Remember to include:
- A title
- A scale (y axis)
- Label each axis.
- Present your work neatly.
- Use ruler to rule all straight lines.
2. When you have competed creating your bar graph, answer the following questions:
- What was the most favourite flavour of ice-cream?
- What was the least favourite flavour of ice-cream?
- What two flavours had the same amount of tally marks?
Extension: IXL Activities-
Grade 4: H.6, H.7
Grade 5: Q.4, Q.5
Grade 6: CC.10, CC.11